UFS vs eMMC: Which is Better?
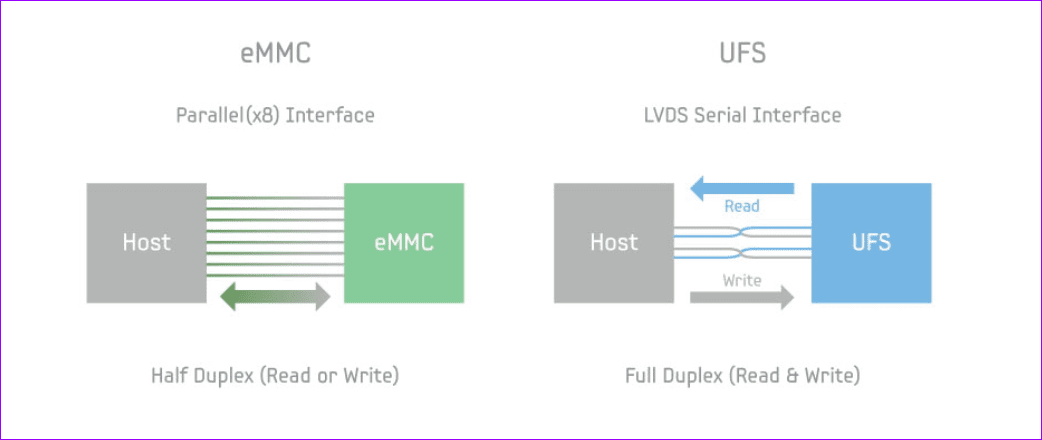
Architecture
UFS, unveiled by standards body JEDEC, is a storage solution that determines how the storage chip of a device connects and exchanges information with the rest of the system. This system is responsible for speeding up the data transfer, app load time, and also the app installation time on most phones. And contrary to popular thinking, UFS is not just limited to smartphones.

It is also used in car media players, VR systems, and Chromebooks. The first iteration of UFS was announced in 2011, and the UFS 2.0 standard was published in 2013. The UFS 3.0 standard was unveiled in January 2018, and UFS 3.1 made its debut in January 2020. The latest version, UFS 4.1, was launched in 2022.

On the other hand, the MMCA (MultiMediaCard Association) was introduced eMMC in 1997 and is a traditional storage solution. However, it’s still stable and dominantly used in several consumer electronics, such as e-readers, smartphones, and tablets. The latest version is eMMC 5.1, which was announced by Samsung in 2015.
On a more technical level, eMMC is an advanced NAND flash memory that bundles a controller apart from the flash memory.
Performance
Before we get down to it, let’s make one thing clear. The storage solutions were designed for faster file copying to improve your overall usage experience on phones and other devices. When it comes to the first generation UFS, it provided 3-fold faster read-write speeds than its counterpart.
If we talk numbers, UFS 3.0 offers sequential reads of 2,100MB/s while writing the data at a speed of 410MB/s. This was succeeded by UFS 3.1, which offers a higher sequential write speed of 1,200MB/s while retaining the same 2,100MB/s sequential reads. The latest version, UFS 4.0, offers a whopping 4,200MB/s and 2,800MB/s of sequential read and write speeds, respectively.
On the other hand, eMMC 5.1 runs at a snail’s pace of just 250MB/s for sequential reads and 125MB/s for sequential writes. Compared to eMMC 5.1, UFS 4.1 is about 16x faster in sequential reads. All these numbers eventually translate into better multitasking and faster turnaround time. This boost in speed can be seen when you open a new app or capture a high-resolution photo or a 4K video.
What About RAM?
A smartphone’s performance depends on many factors, and the RAM (Random Access Memory) plays a vital role in it. In the simplest terms, RAM is used by apps and games to rapidly move around huge chunks of data between the processing core and the file system.
It also prevents apps and games from making frequent calls to the file system or core to reduce the turnaround time for a call. For example, if you are playing a graphics-intensive game like Fortnite or PUBG, there is plenty of data that the phone needs to move around, and here. the RAM acts as a temporary data storage.

That’s where RAM with a higher bandwidth like LPDDR3, LPDDR4, LPDDR4X, LPDDR5, and LPDDR5X comes into the picture. These memory management systems allow for a higher amount of data to be moved and are accompanied by low power consumption. The newer LPDDR5 RAM can theoretically reach speeds up to 8,533Mbps. Meanwhile, the previous generation LPDDR5 provided a maximum speed of up to 6,400Mbps.
When it comes to a phone’s performance, both the RAM and the UFS complement each other. This is especially true when it comes to running memory-intensive jobs like playing 4K videos, taking burst photos, or playing high-resolution 3D games.
FAQs
Upgrading from eMMC to UFS is generally not possible as these storage types are soldered onto the device’s motherboard. To benefit from UFS storage, you would need to purchase a device that already comes with UFS pre-installed.
UFS storage can be more power-efficient due to its faster data transfer rates, which means it can quickly complete tasks and return to a low-power state sooner. However, in the real world, there are plenty of other factors that have a more significant impact on battery life.
Smartphones still use eMMC storage because it is cost-effective and sufficient for basic tasks, making it ideal for budget and mid-range devices. It helps manufacturers keep prices low while providing adequate performance for everyday use.
Yes, UFS is worth it for users who need faster data transfer speeds, better multitasking, and improved overall performance, making it ideal for high-end smartphones and demanding applications. It enhances the user experience significantly compared to eMMC.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 09 July, 2024
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.